|  |  |  |  | 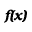 |  |  |  |  |  |
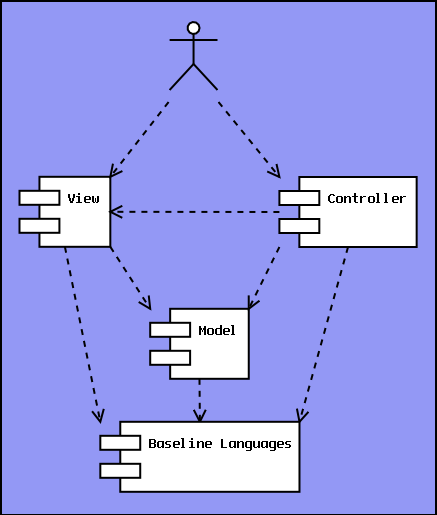
Model-View-ControllerModel-View-Controller is a widely used Architectural Pattern. The program is split into three Components. The Model contains the program state, the Controller executes user actions and the View displays information for the user.
This pattern is not quite compatible with LISA.
This leads to the following drawbacks:
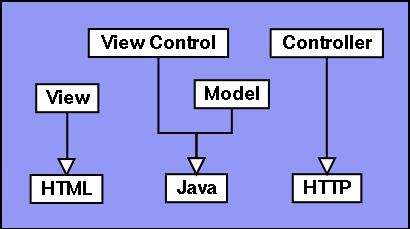
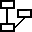
Here is a possible Language inheritance graph for a web application implemented with Java servlets.
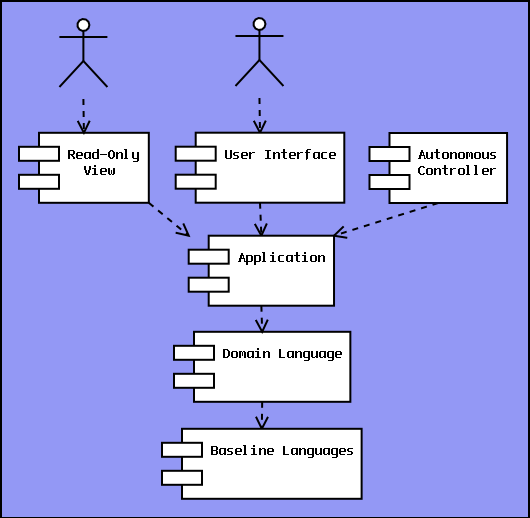
MVC is monolithic and not made for reuse. The entire structure is basically one Language, and as the Language mainly interacts with the user, the conclusion is that MVC is just a large User Interface and Application mixed together with a polluted Domain Language at the bottom. This kind of messy architecture is what LISA is built to avoid. The pattern may feel intuitive when looking at it from a functional breakdown perspective, but when looking from the Language definition perspective, it doesn't make sense. Note that MVC's ability as a Design Pattern is not examined here. Upon examination, it may turn out to be a good Design Pattern, or similar deficiencies will be detected in this domain as well. MVC improvedWith some minor modifications, MVC can be transformed into a better pattern, retaining the qualities the original pattern tried to offer. The architect considering MVC wants to have multiple views and controllers interacting with the same Application. The conclusion above was that the controller and the view can't be separated in a clean way. The solution is to let any Component interact with the Application, and combine view and controller functionality in the same Component when necessary.
|
Related Topics
Application Architectural Patterns Design Patterns Domain Language LISA Language User Interface |
| Copyright (C) 2003, Marcus Andersson |